Traffic Flow Sampling in Juniper Mx-5 and Mx-480 Routers IPv4 and IPv6
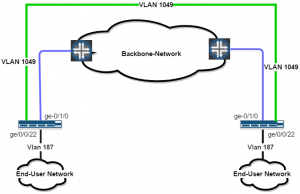
Traffic Analysis is a critical component in network planning, security and troubleshooting. For you to perform traffic analysis, you need to collect network traffic flows from the different aggregation points in your network such as routers and switches.
In Juniper, they take advantage of ‘sampling’ packets and frames going through a switch or router. The sampled flows can used by third party applications such as nfsen and ntop.
This configuration solution was done on a Juniper Mx 5 Router using ipfix .
Create a sampling instance at the chassis level in this case it was named ‘1to1’
set chassis tfeb slot 0 sampling-instance 1to1
Place the flow table size at the chassis level on tfeb for both IPv4 and IPv6
set chassis tfeb slot 0 inline-services flow-table-size ipv4-flow-table-size 5
set chassis tfeb slot 0 inline-services flow-table-size ipv6-flow-table-size 5
Continue reading “Traffic Flow Sampling in Juniper Mx-5 and Mx-480 Routers IPv4 and IPv6”